This was an interesting find during the Archived Case from ILN. Focus was on western portions of Indiana/eastern Ohio at several areas of rotation associated with a multicellular cluster of convection. A tool commonly used to interrogate a potentially tornadic storm’s rotational velocity is the VRshear tool. This tool calculates the Vrot, line distance (end of points), shear (in ms-1) and distance from the RDA. WDTD mentions from their Impact Based Warnings Guidance of around 30kt of rotational velocity being the initial supercell tornado warning threshold. Of course, this has some gray area but is generally expressed as an approximation.
At 0207Z from KILN, a cell was identified to show increasing cyclonic rotation. Vrot was calculated to be at 37kt estimated. NDTA probabilities began relatively low at 21.48% which at this early indication, a warning would have already been required. The next scan at 0208Z showed an increase of Vrot to 38kt, with NTDA probability increasing to 24.85%. One more minute followed at 0209Z showed an obvious increase in Vrot at 44.7kt with NTDA Probability of 32.41%.
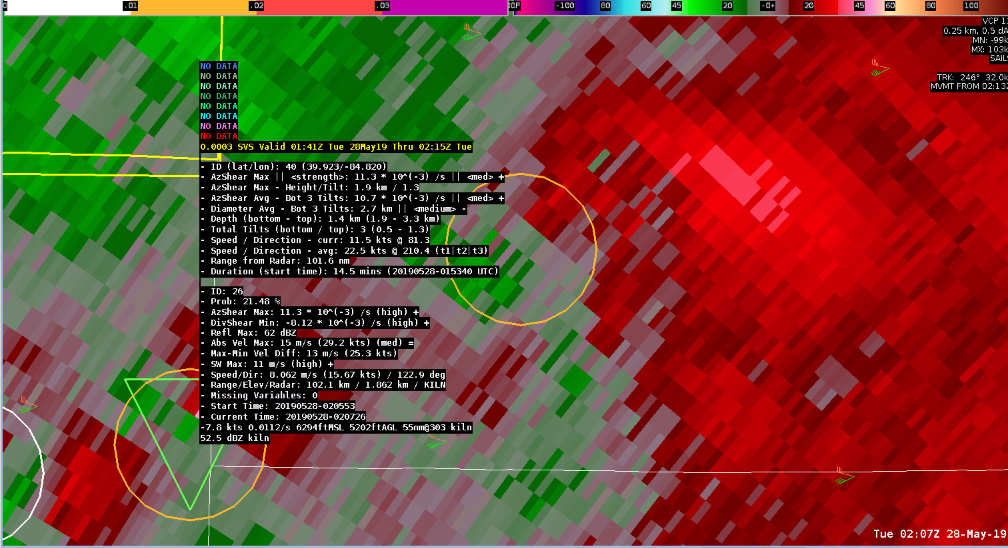
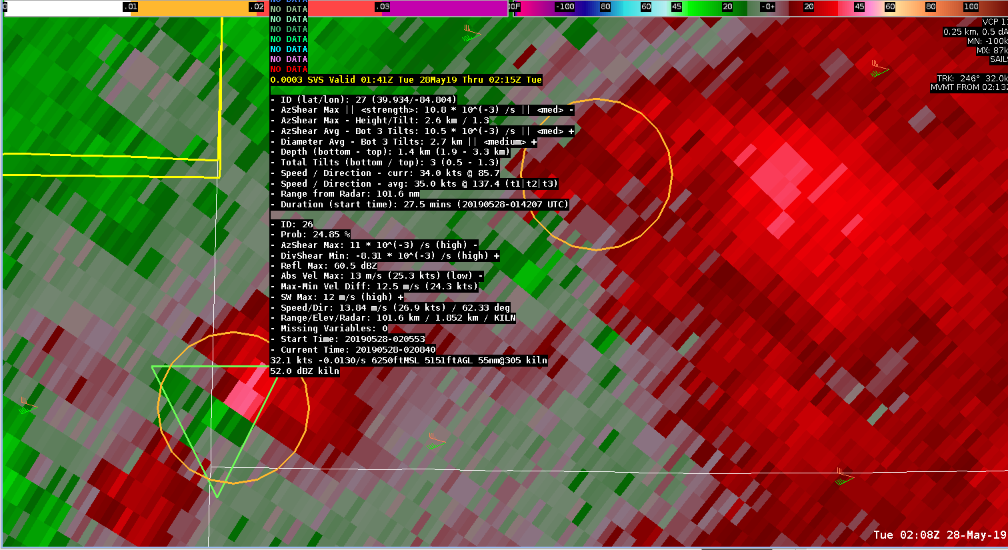
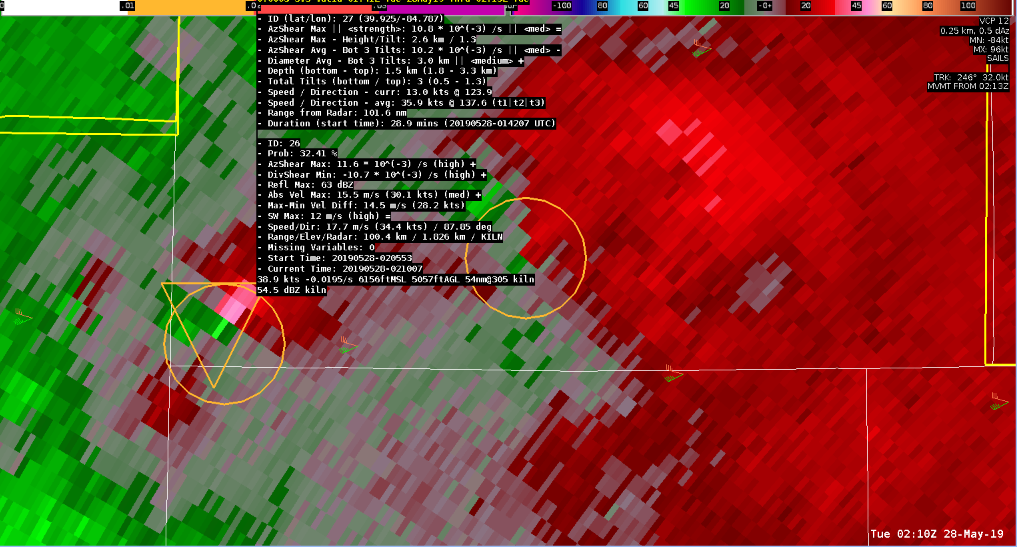
This is one of several examples where lowering the current default threshold of 30% was necessary. While tracking of both NMDA and NDTA was very accurate, I was surprised at the lower probabilities. A few calculated parameters were identified to be a potential hindrance at a higher probabilistic value, including high SW (and trending higher) and AzShear Max value actually showing a temporary lowering trend at 0207Z. An interesting situation where having to lower the probabilistic threshold was necessary, and was a bit lower than what was expected but still showed consistency with tracking.
– Dusty Davis
