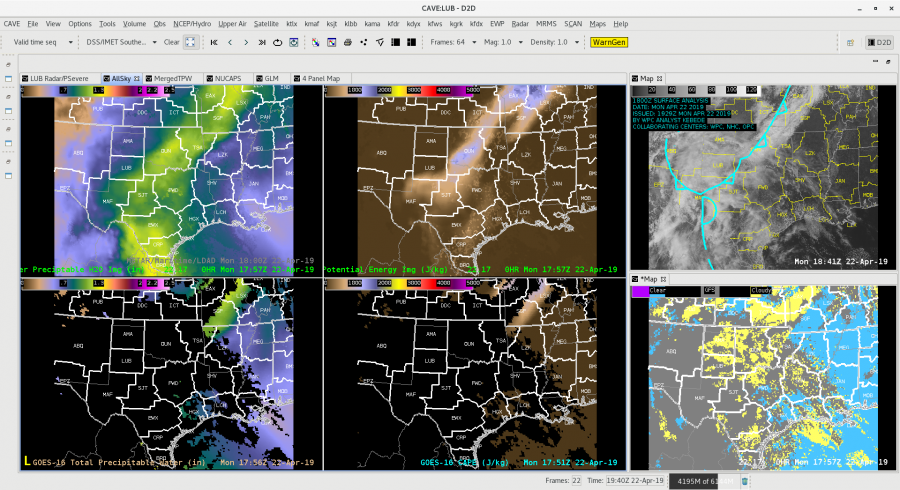
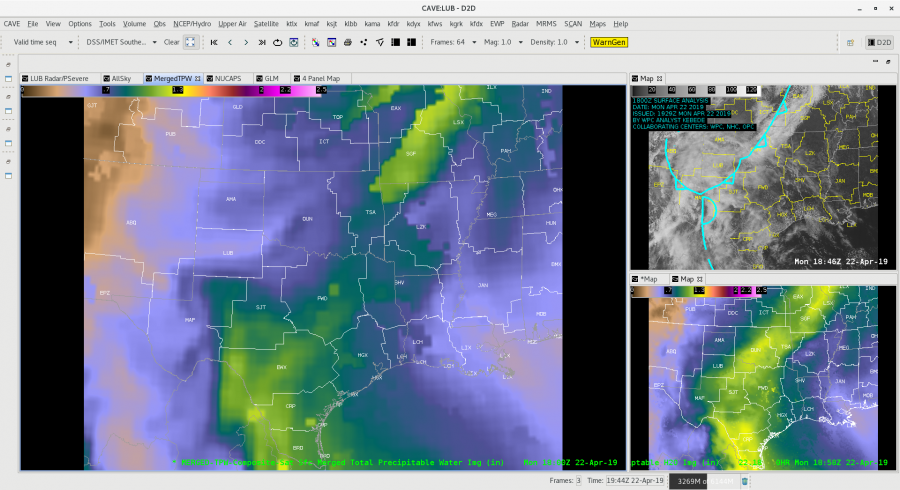
Did a quick check of the merged TPW and AllSky products and as previously advertised/anticipated, the convection has been riding right along the gradient of the higher instability, but there is some discrepancy as to whether it’s right in the heart of the higher PWATs or along the leading edge, depending on if you’re looking at the AllSky or TPW, respectively. Noticed quite a bit of a latency in the availability of these products (up to an hour), which wouldn’t be good in an operational setting. Compared the values of the TPW and AllSky PWAT with the RAP, and the AllSky matched up much closer to the RAP. However, with the amount of cloud cover in the region (for obvious reasons), the GFS is the predominant data type (basically a model-to-model comparison). Either way, the general idea/trend is helpful if serving as a mesoanalyst in an operational environment.
~Gritty
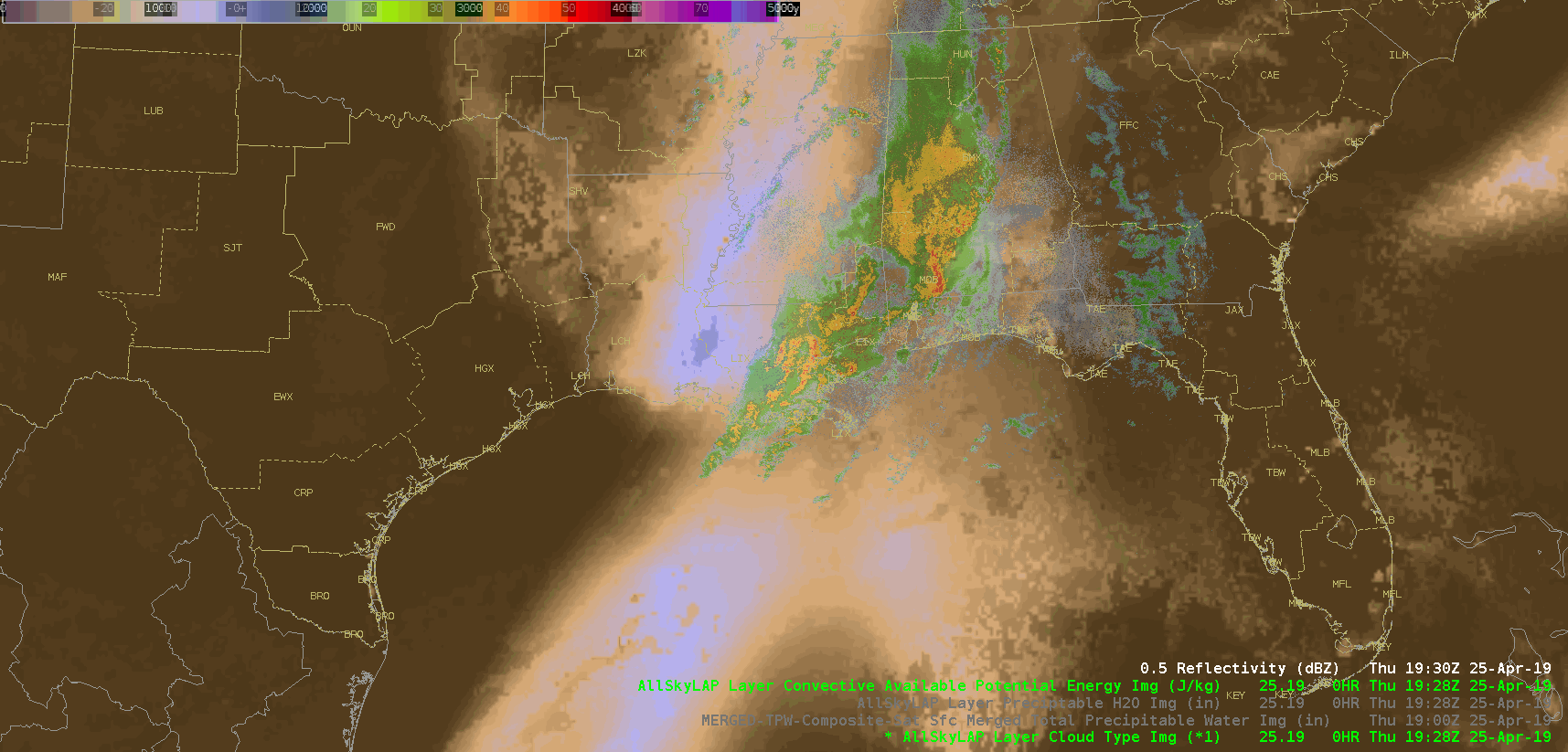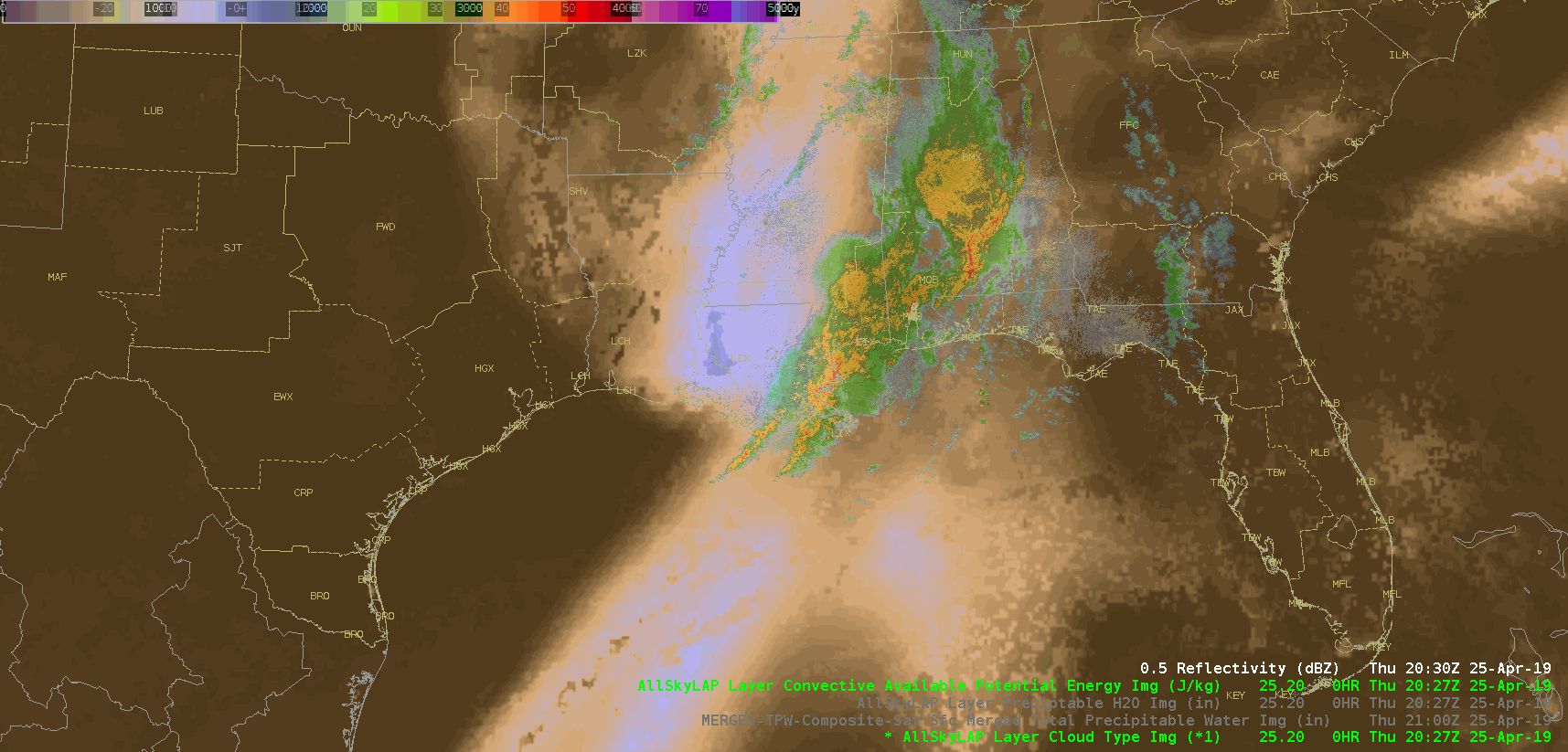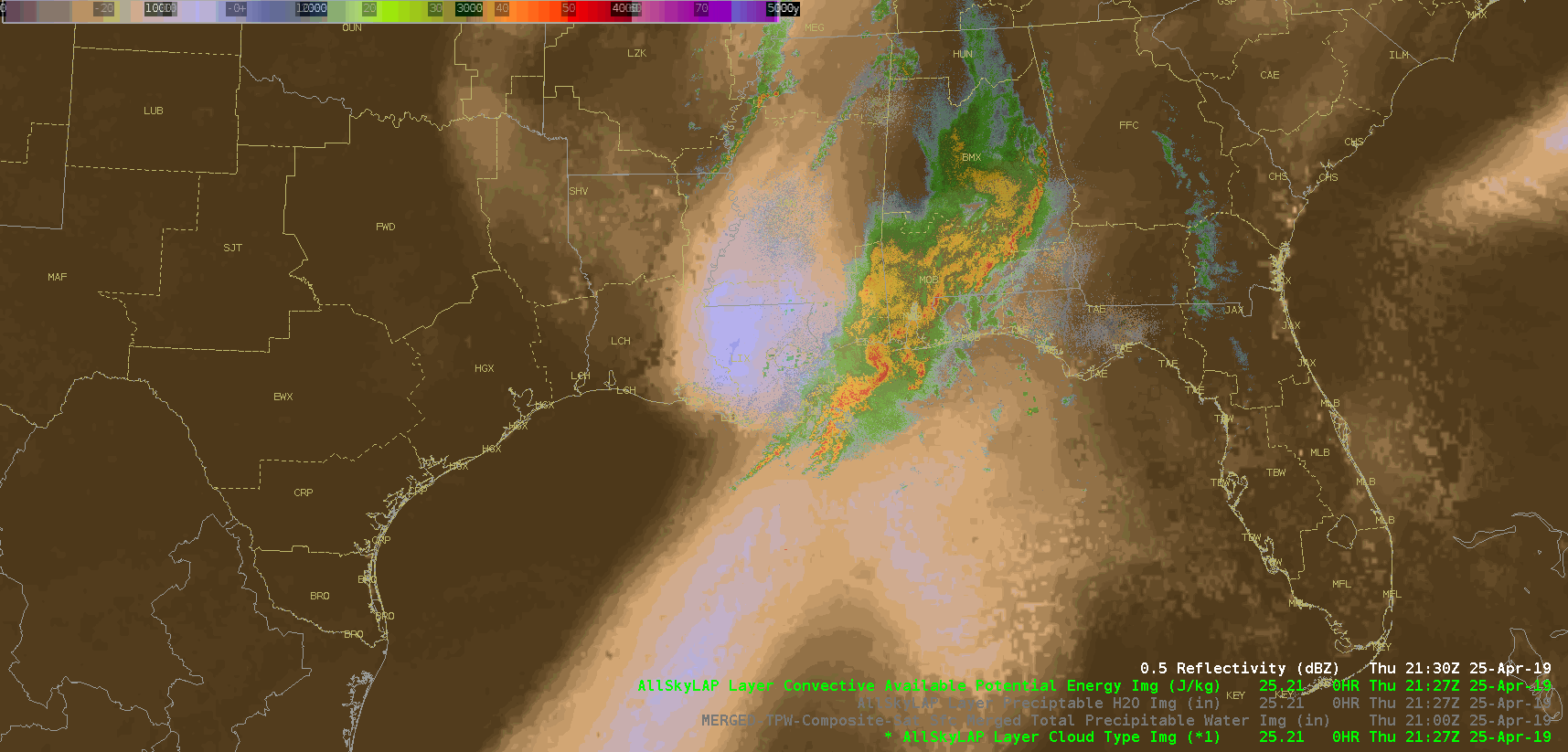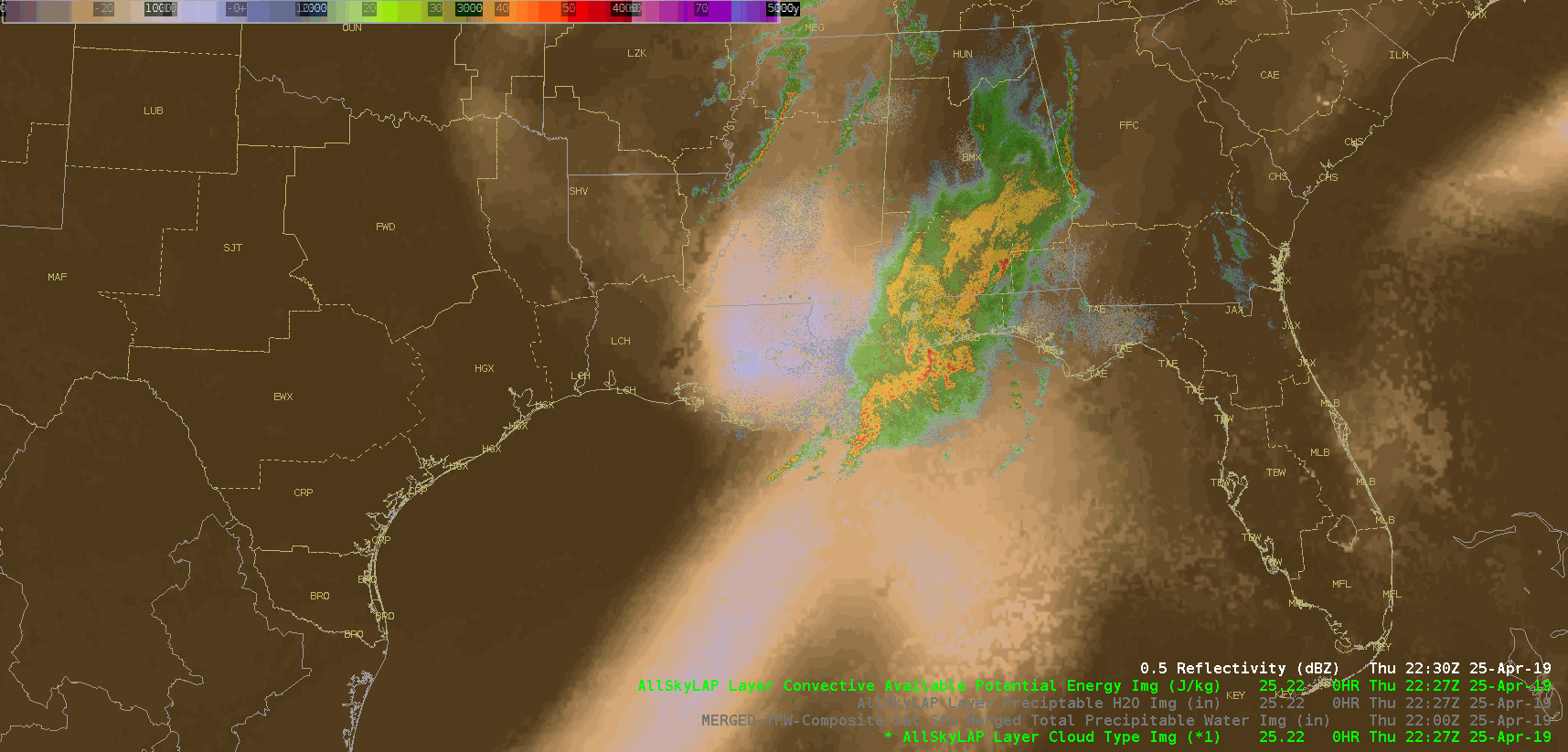
(CAPE)
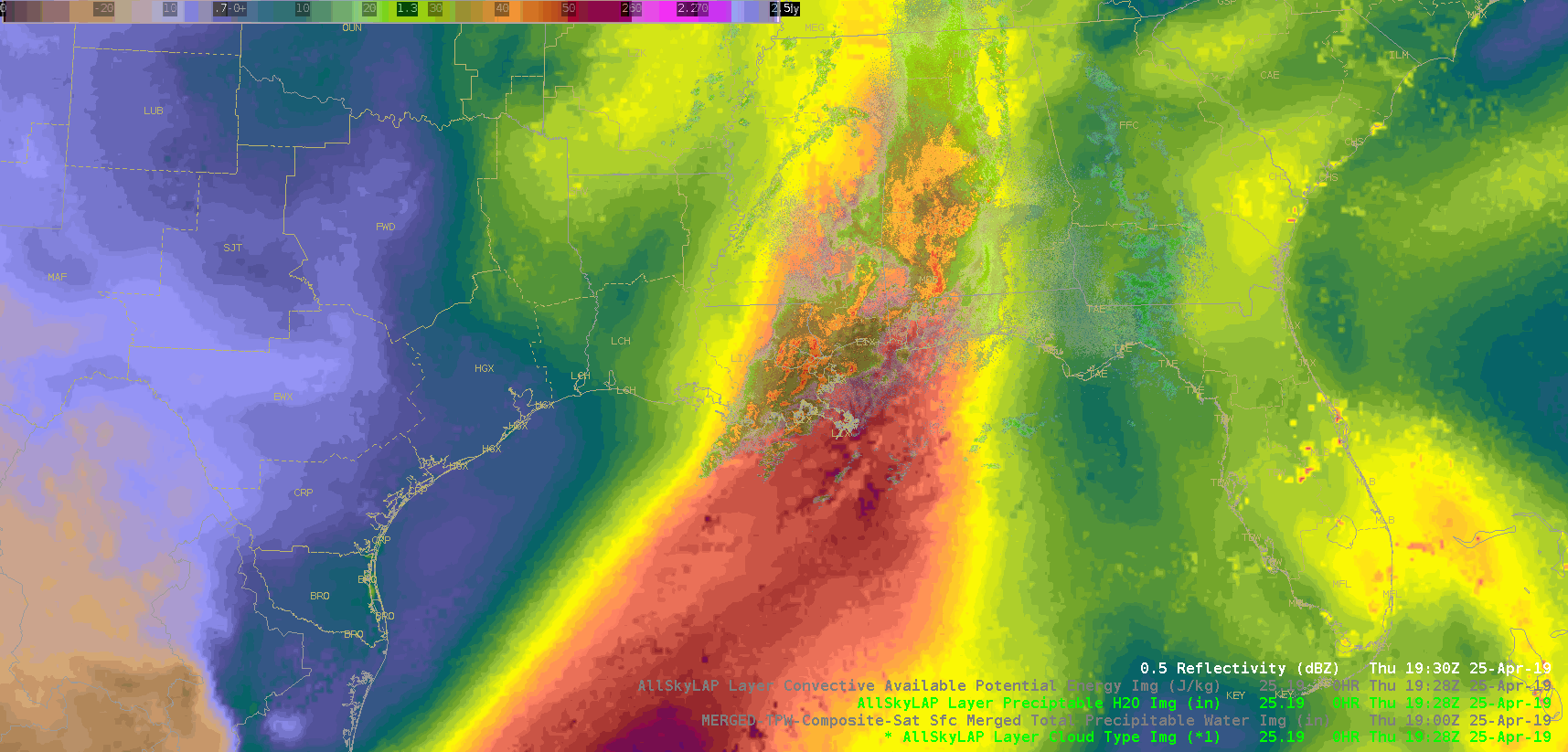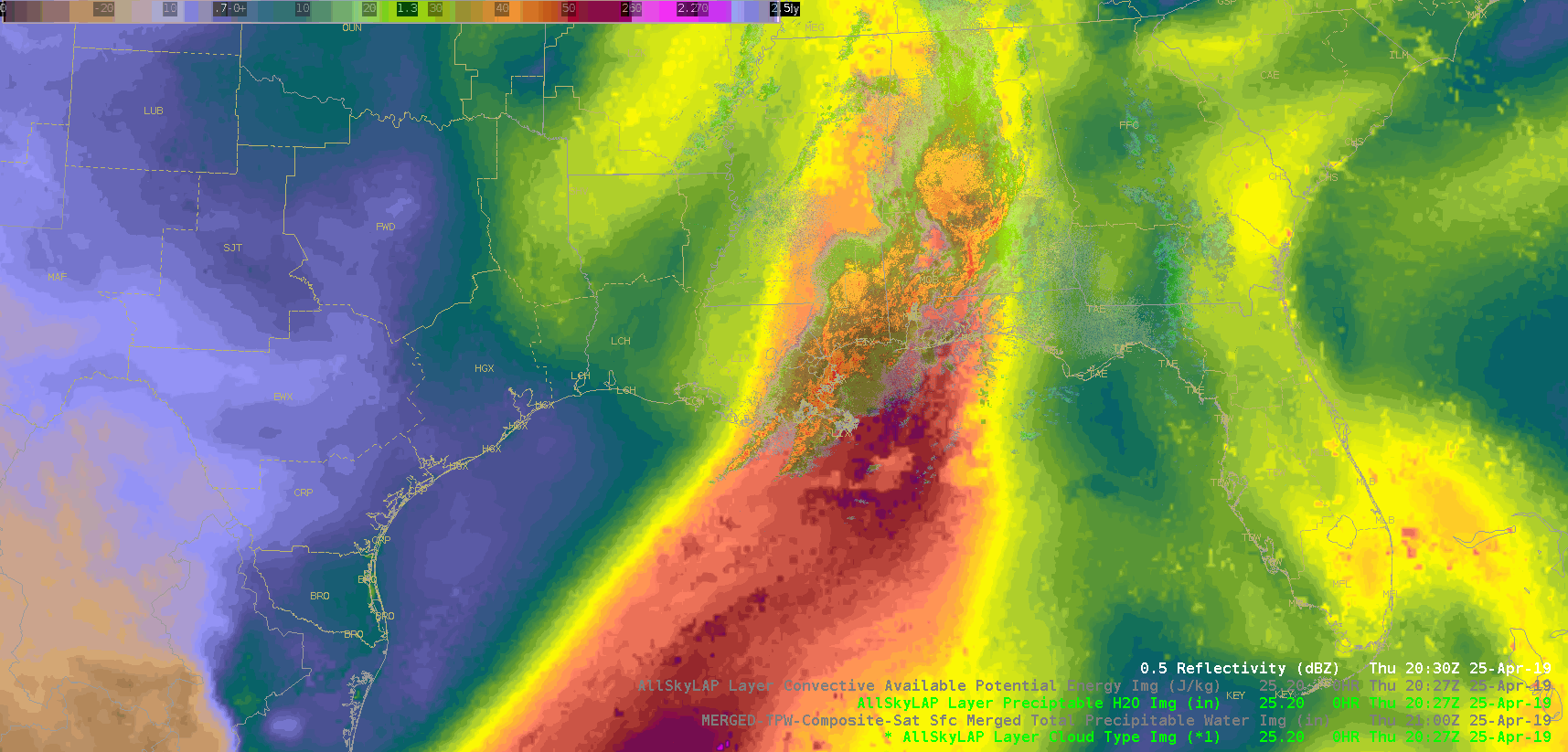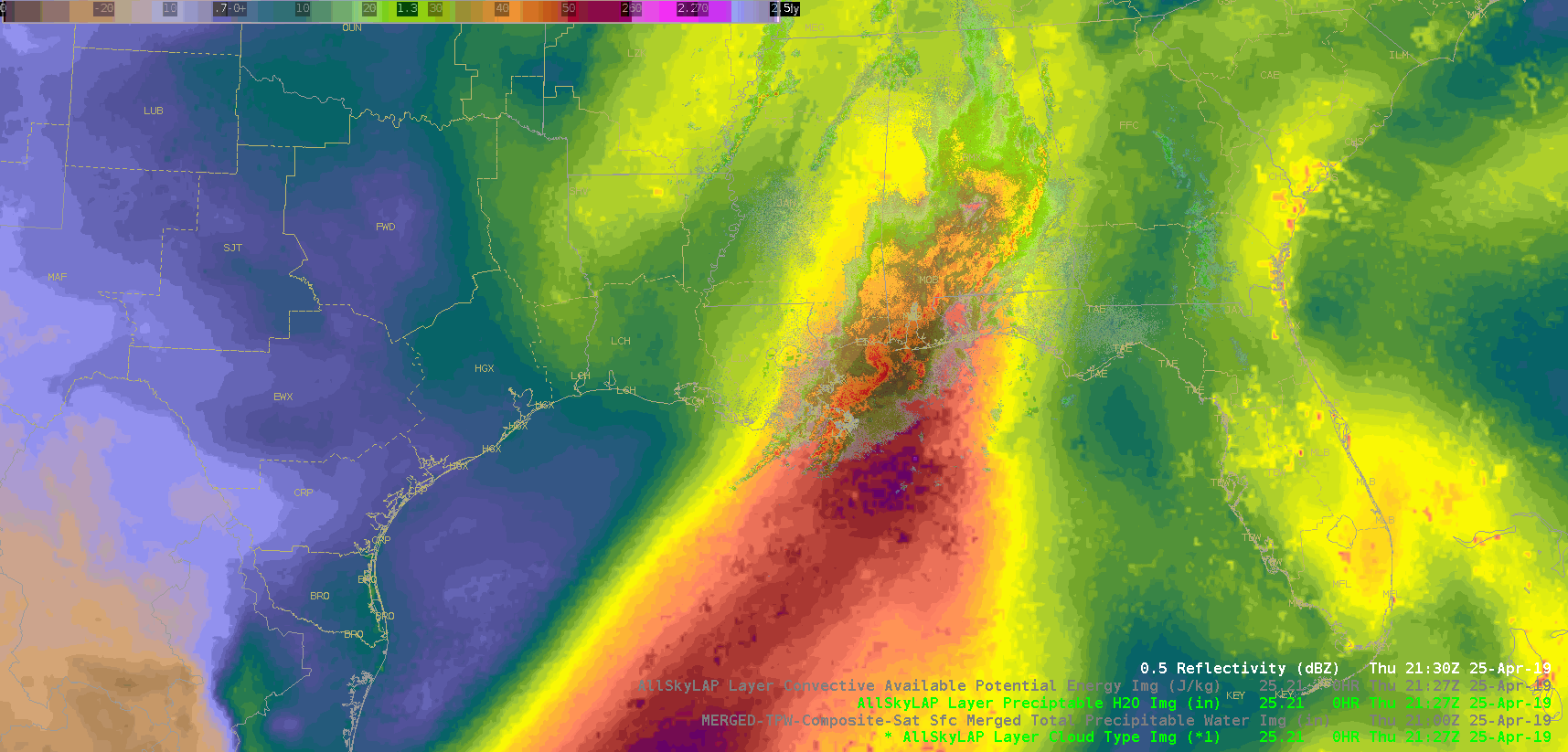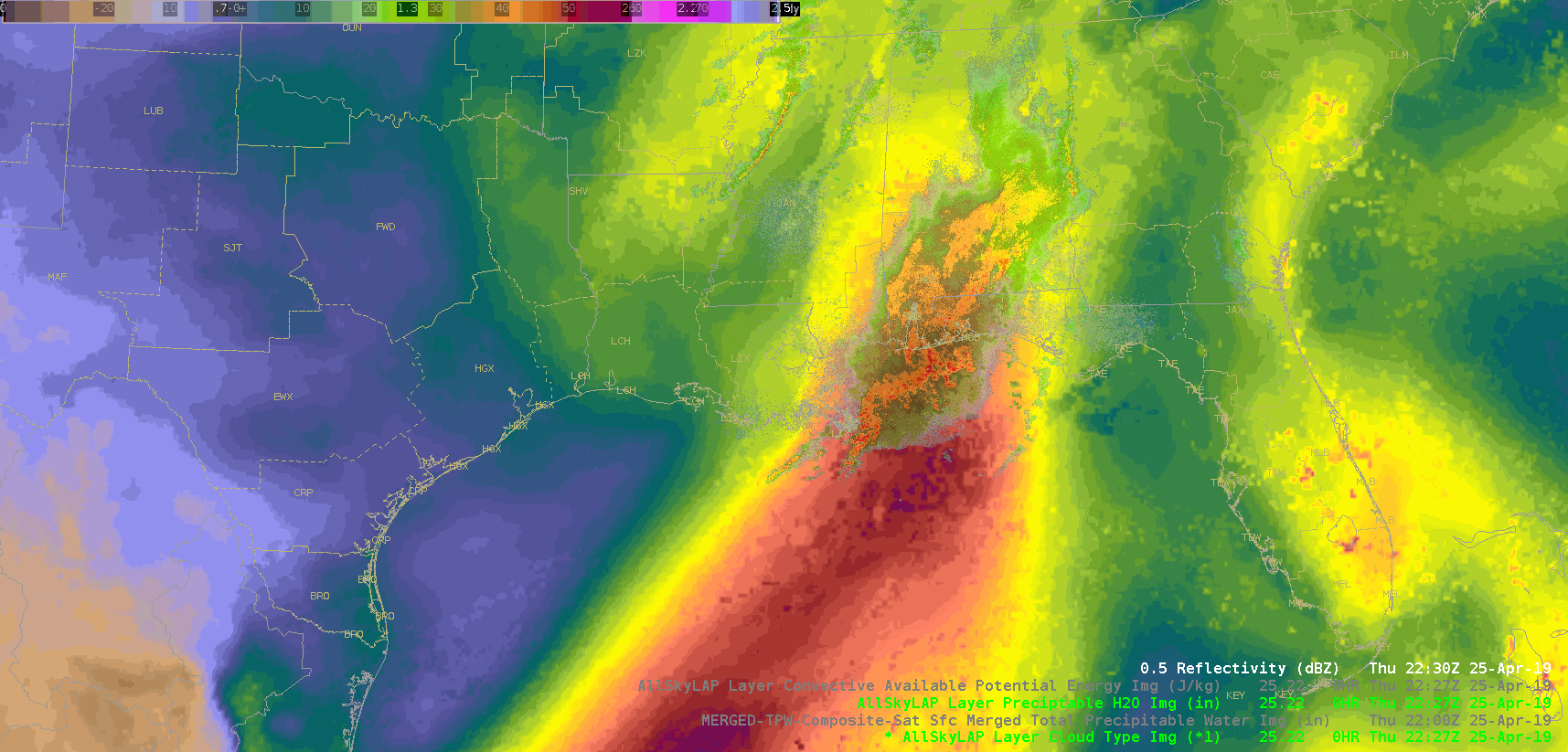
(AllSky PWATs)
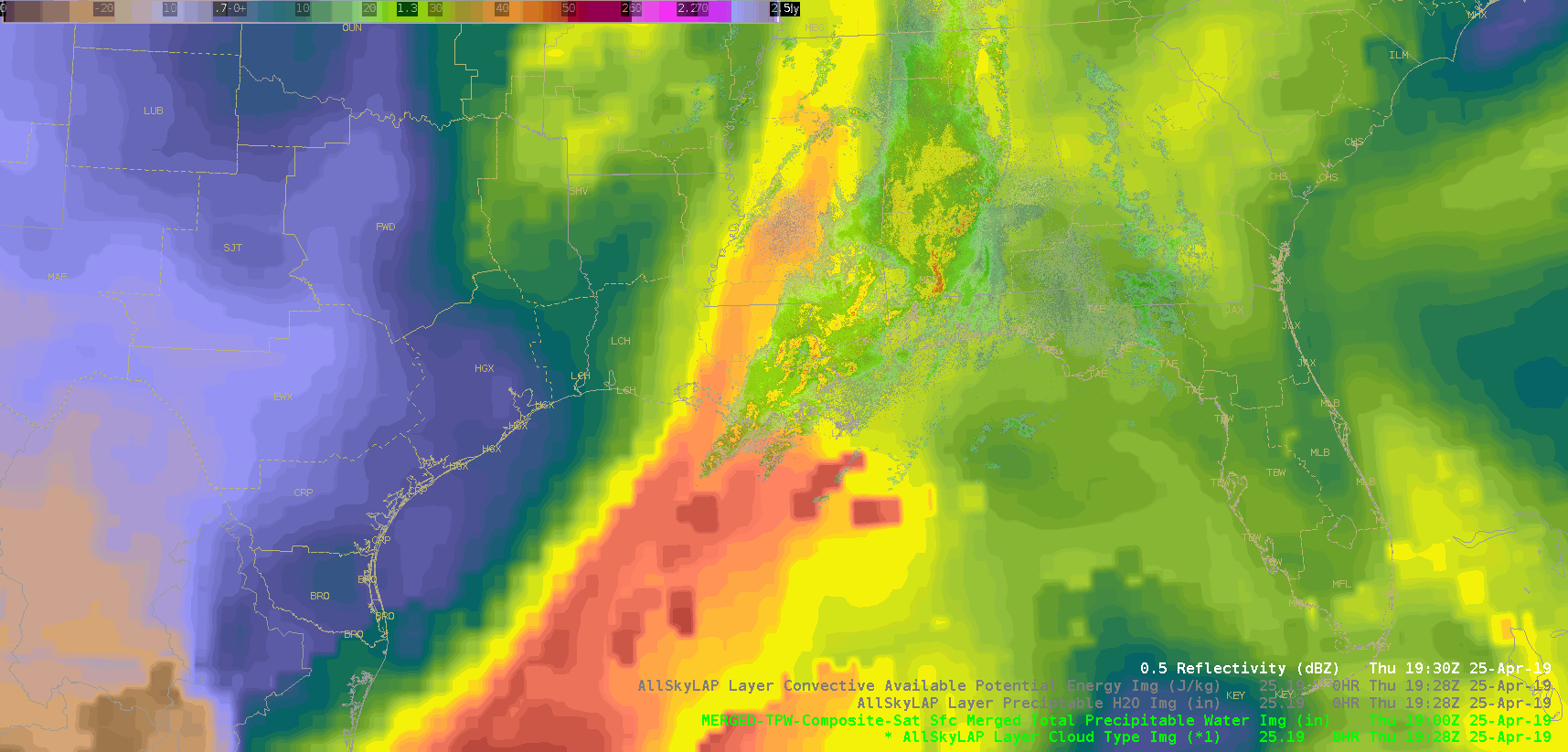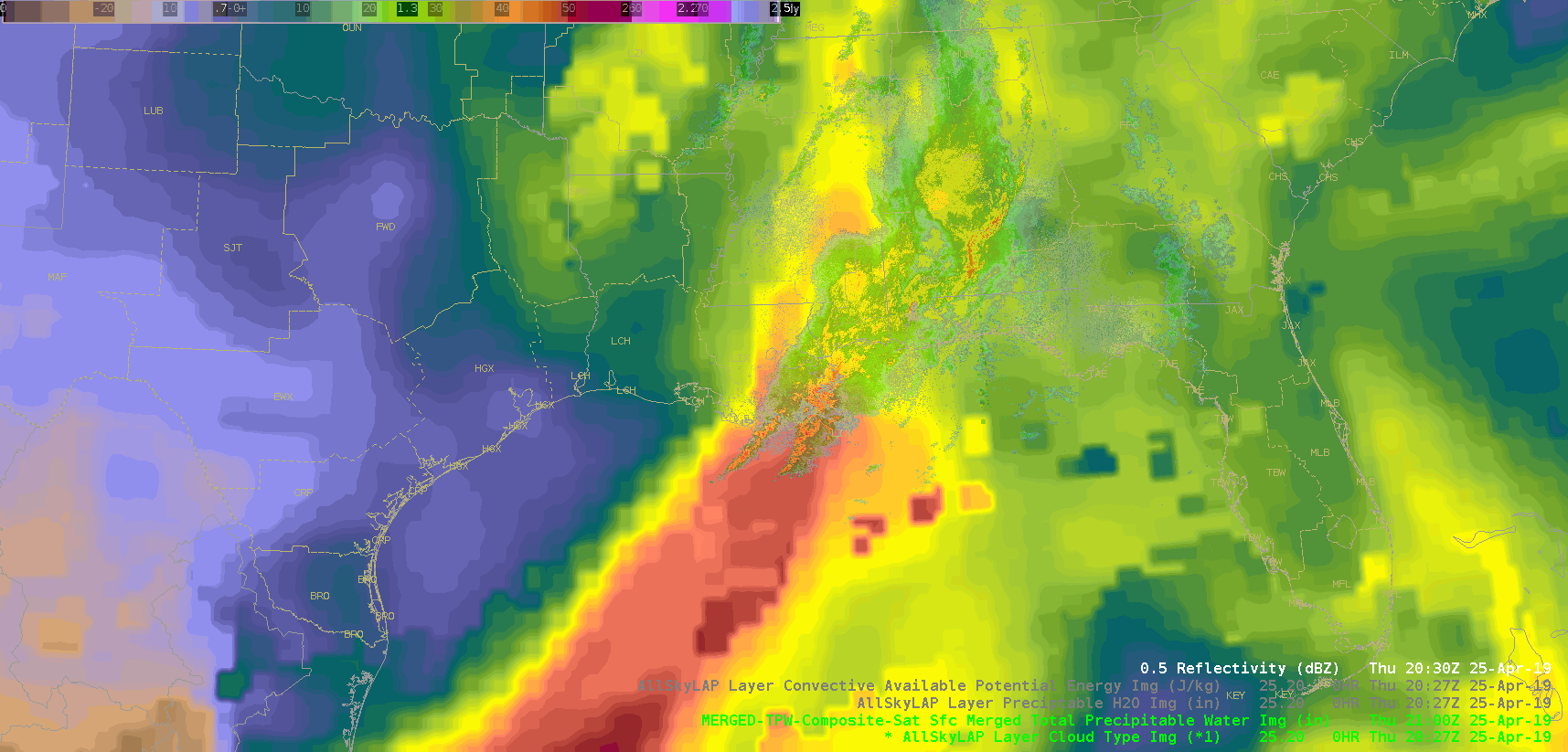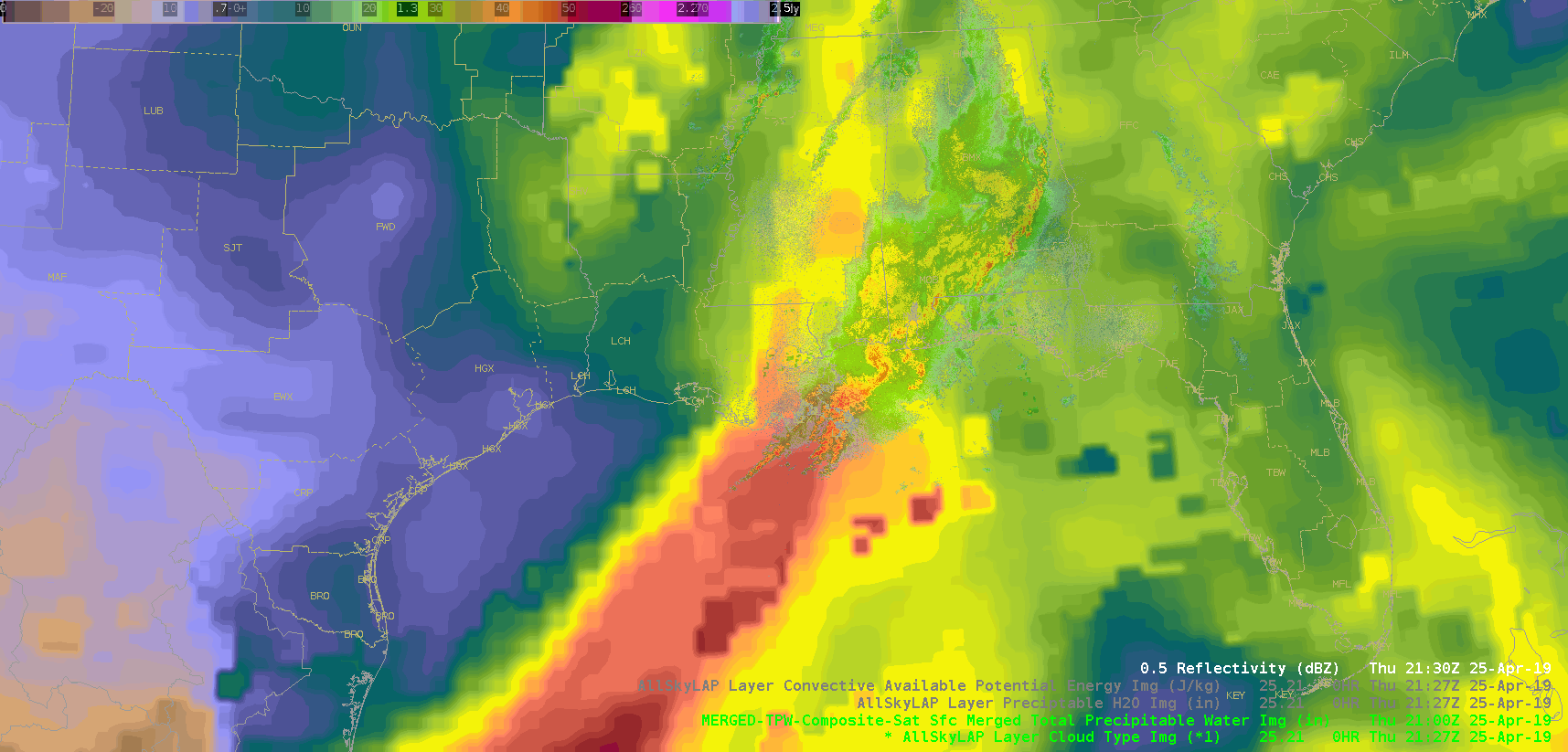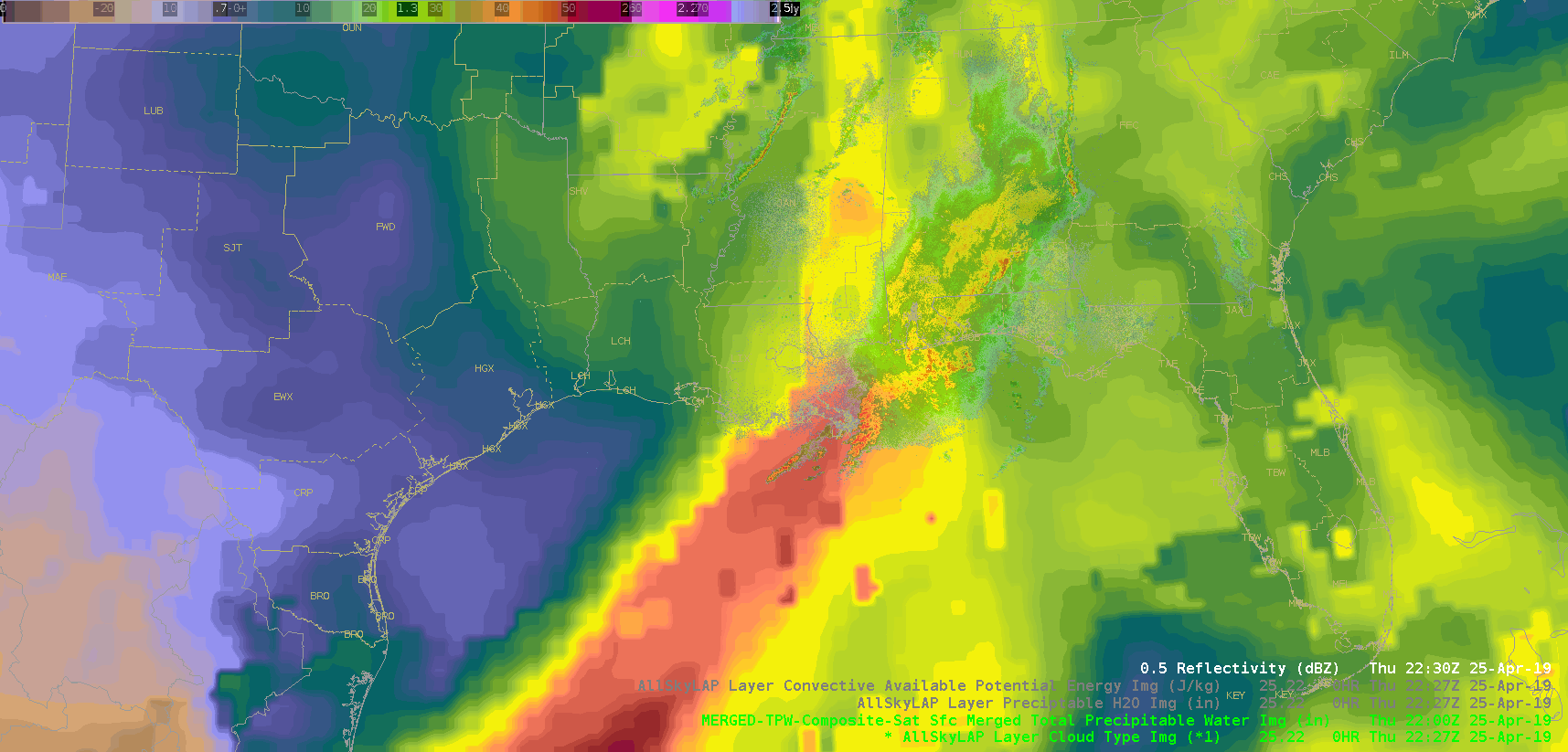
(Merged TPW)


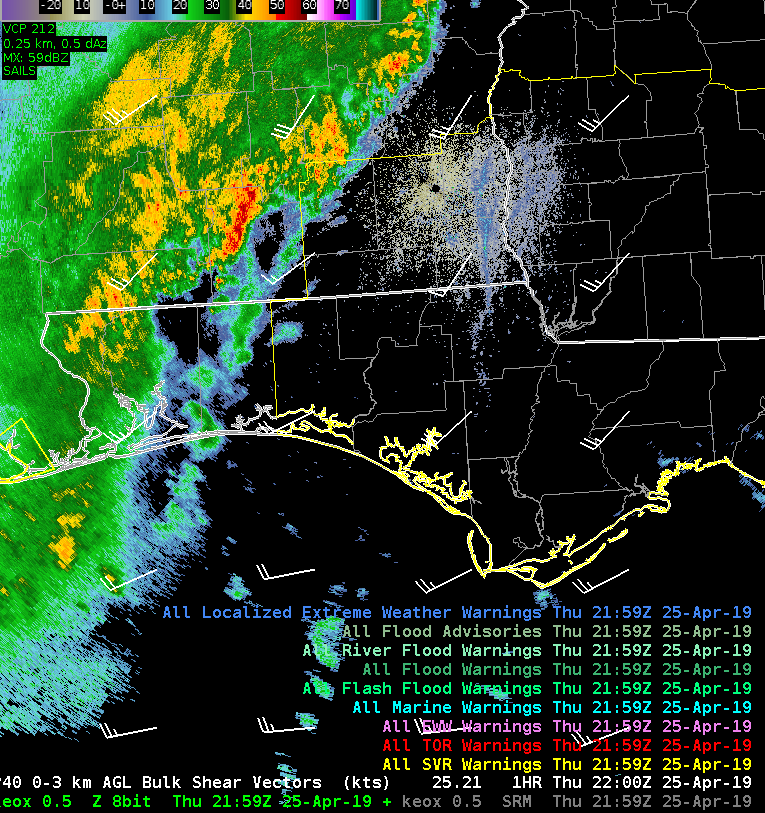 The layered TPW product shows a tongue of moisture approaching the region. It looks like a line of towering cumulus developed over the Gulf of Mexico as this moisture interacted with the convergence line.
The layered TPW product shows a tongue of moisture approaching the region. It looks like a line of towering cumulus developed over the Gulf of Mexico as this moisture interacted with the convergence line.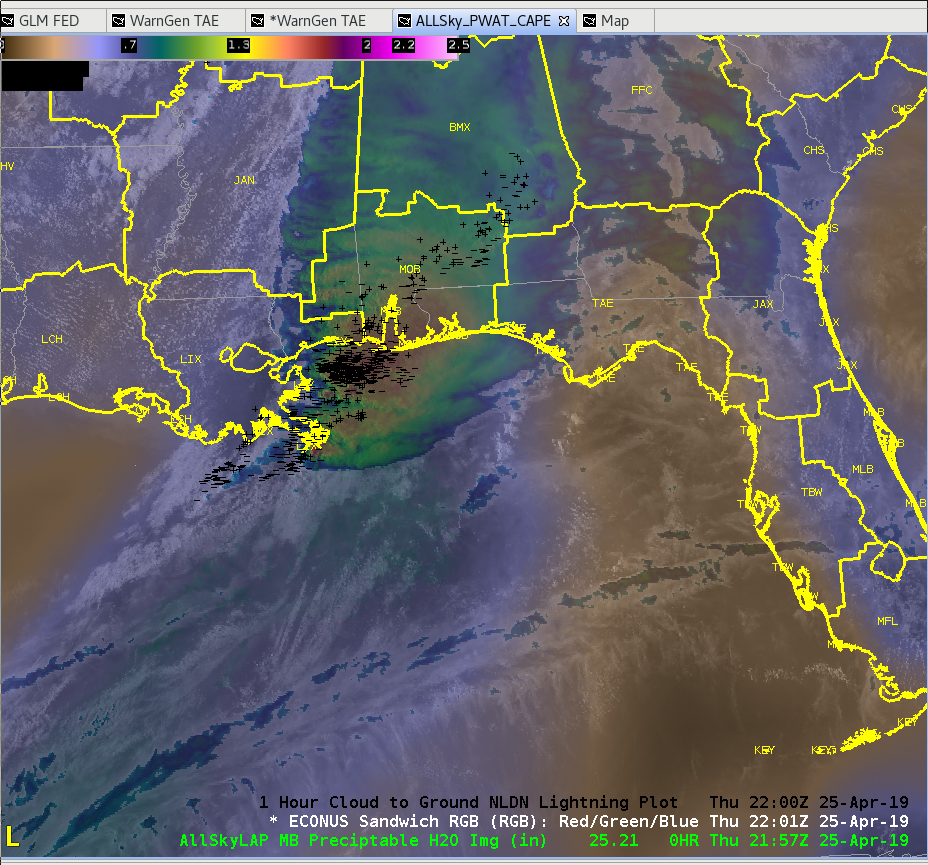 Sandor Clegane
Sandor Clegane