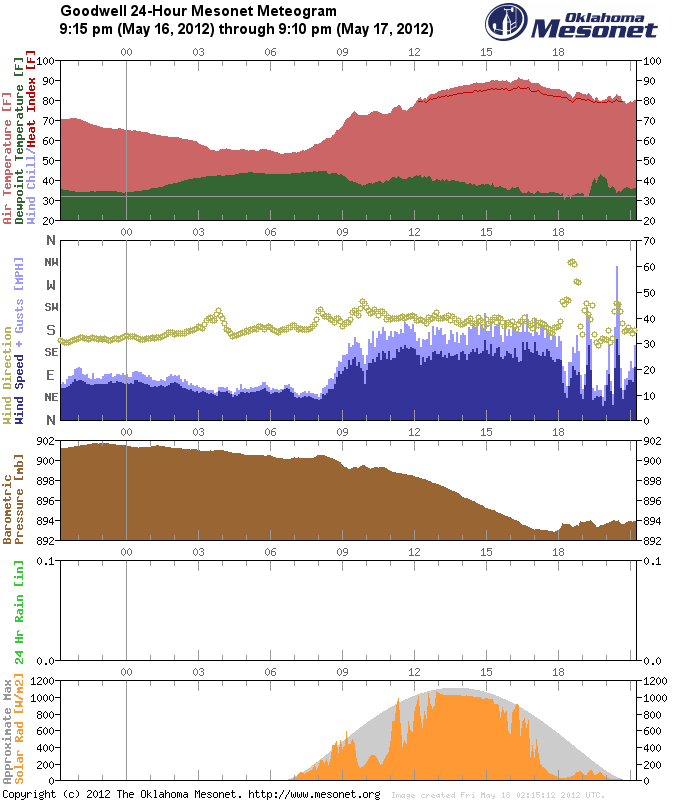
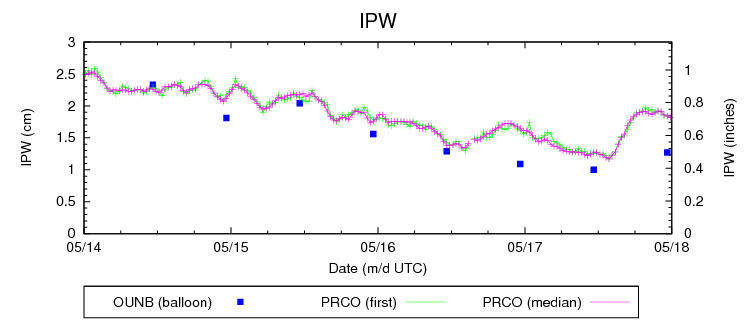
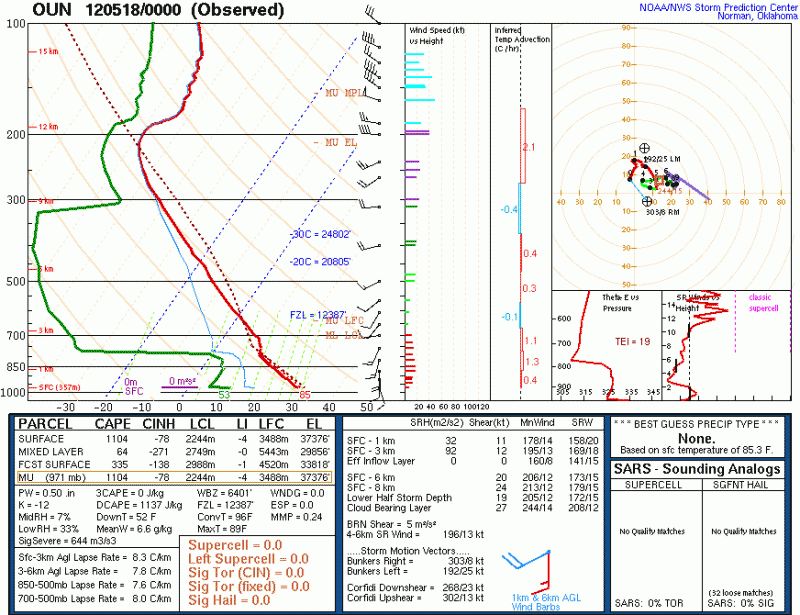
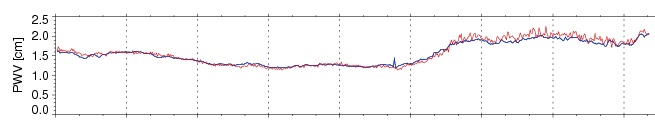
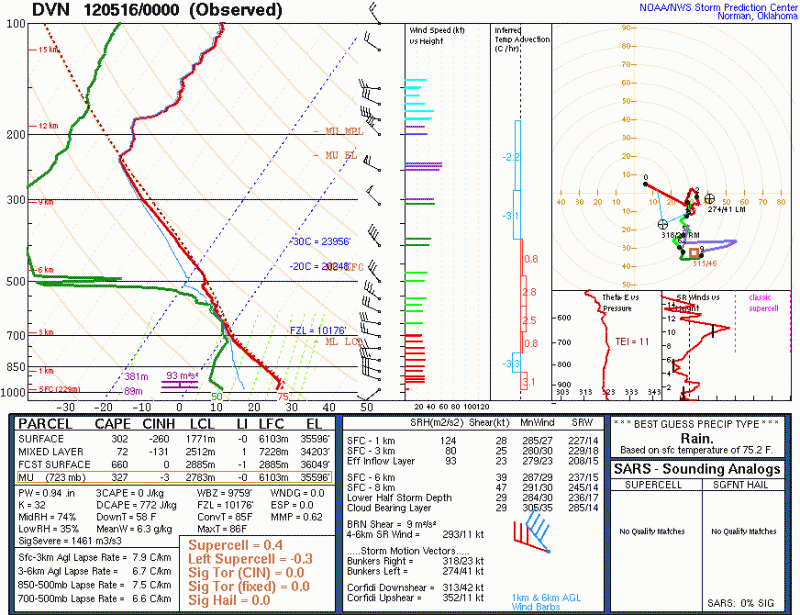
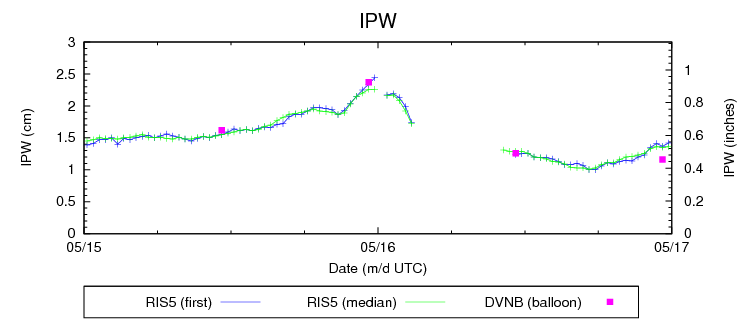
One of the many struggles with forecasting is verification, especially of “rare” events. In the severe storms world, we have storm reports. It has been shown that there are serious flaws with this database over time. They are conditional upon hitting something or someone; population density or highways. There are many areas un-accessible that may have had things like hail or high wind but yet there are no observations nearby. In the Plains this is a big challenge.
Over the course of the HWT EFP, we have debated over the so-called practically perfect methodology. At is core it is a Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) technique using a gaussian smoother (120 km) and a radius of influence technique (40 km) to map individual storm reports to a grid and produce probabilities of severe.
Given that storm reports are not the most ideal, independent, non-biased dataset out there we look to other more unbiased data. So what are the alternatives? Can we use severe storm warnings? How about data specifically from the radars like Max Estimated Hail Size or Rotation tracks? How about satellite derived data about vegetation?
Just about all of these data sets have their own problems. For the radars, we are observing rotation or hail aloft, not necessarily at the ground. This is still valuable information. But how do we switch from spotty storm reports to continuous tracks? Will the same KDE smoothing approaches be necessary?
For the warnings, it is clear that meteorology alone is not driving them. If there is a chance a storm could be severe over a highly populated area at a critical time, the edge goes to issuing warnings as opposed to not. This is not all that bad, since we would all like to err on the side of safety. Better to be safe than sorry.
Using radar data we still have to verify that what the radar detects is actually occurring at the ground and that phenomena is as strong/large as indicated aloft. And that requires doing verification on the observations. The SHAVE folks at NSSL-OU are trying to do exactly that as are some other NWS associated folks, though at the moment their name escapes me.
Satellite data also offers some advantages on tracks of severe storms provided there is damage say from large hail stripping vegetation bare or tornadoes doing damage. Collecting more fine resolution data is going to take a dedicated effort but in the end it helps build more complete knowledge about storms, more understanding about the successes and failures of the forecasts, and quite possibly will end up making better forecasts.